The USAID-IMA World Health Counter-Gender Based Violence Program (USAID-IMA CGBV Program, or “Tushinde Ujeuri” in Swahili) is a comprehensive program to help communities respond to and prevent gender-based violence in the Democratic Republic of Congo. The United States Agency for International Development-funded program is made possible by the generosity of the American people and implemented by IMA World Health.
This project is a key USAID initiative in Eastern Congo where years of insecurity and conflict alongside deeply rooted gender inequities and harmful cultural practices have contributed to high rates of sexual and gender-based violence. As a five year project (November 2017 – October 2022), the USAID-IMA CGBV Program aims to strengthen community-based prevention of and response to GBV in eastern Congo; effectively reducing GBV incidence and improving the quality of and access to holistic care for survivors, particularly among vulnerable groups. The project works in an integrated manner to achieve three intermediate results:
- target communities demonstrate greater acceptance of positive gender roles;
- availability of community-level GBV-related services improved; and
- perceptions of stigma surrounding reintegrated survivors reduced.
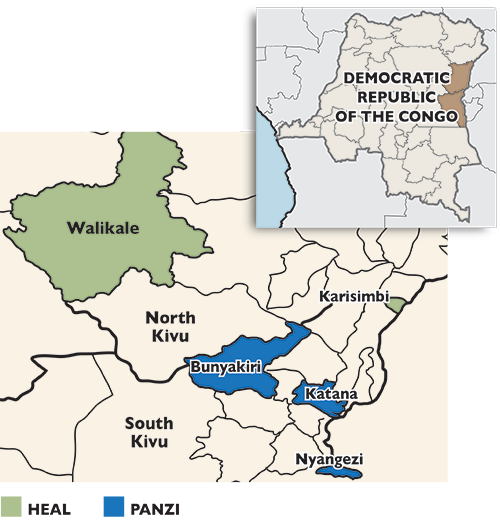
Partners and implementation areas
IMA World Health implements the USAID-IMA CGBV Program in partnership with a consortium of technical and implementing partners. HEAL Africa leads implementation in two health zones in North Kivu (Walikale and Karisimbi) while Panzi Foundation leads implementation in three health zones in South Kivu (Bunyakari, Katana, and Nyangezi). The American Bar Association-Rule of Law Initiative (ABA-ROLI), Search for Common Ground, University of Washington, Johns Hopkins University, and Overseas Strategic Consulting, Ltd. provide specialized technical assistance.
Key activities
Holistic Care for Survivors of SGBV
The project strengthens health facility capacity to provide comprehensive health services for SGBV survivors, including post-exposure prophylaxis, treatment for sexually transmitted infections and family planning services. Psychosocial counseling as well as cognitive processing therapy, an advanced therapy for survivors experiencing post-traumatic stress disorders and related conditions, are offered to all SGBV survivors. Survivors are also offered socioeconomic support through enrollment into village savings and loans programming, skills-building in literacy, and referrals to other income-generating activities. ABA-ROLI strengthens access to legal and mediation services for survivors seeking justice.
Health-Zone Based Safe Houses/Community Centers
The USAID-IMA CGBV Program establishes centers in all supported health zones to provide expanded services to survivors, empower and support women and community groups, ensure referral pathways, and to serve as a central setting for forums, dialog, and platforms to address the problem of SGBV.
Community-Based Approach to Norms Change
The USAID-IMA CGBV Program works through established community-based groups to roll out evidence-based social and behavior change communication (SBCC) interventions to shift community norms to adopt positive gender roles, while reducing stigma and negative attitudes that prevent acceptance of survivors within communities and families. The expanded approach includes community theatre, mobile cinema, community radio programming, and engagement of youth clubs and schools (code de bon conduit) in raising awareness, promoting gender equity and reducing cultural norms that perpetuate GBV.
Community-Based Trauma Healing
Community-based initiatives to resolve stigma, address issues of trafficking and intimate partner violence, dismantle service access barriers for LGBTI and the disabled, and assure gender equity are core principles of the USAID-IMA CGBV Program. Conflict reduction and resolution activities such as alternative dispute resolution, community reconciliation forums and gender discussion groups will be implemented in all health zones.
Key results
- Overall reduction in GBV prevalence in the project’s targeted areas
- Reduced acceptance of GBV among the target population
- Training and support to at least 700 community-based groups (e.g., youth groups, parenting groups and health committees) annually for community norms change and/or survivor reintegration
- Administration of post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) kits to 100 percent of eligible survivors accessing services
- Establishment of at least one safe house per health zone
Trafficking-in-Persons (TIP) results
- 1,140 healthcare providers received training, technical assistance, or capacity building in TIP victim-centered and trauma-informed services
- 711 TIP survivors received medical services
- 882 TIP survivors received psychosocial services
- 150 TIP survivors received legal assistance
- 683 TIP survivors have been reached by more than one service
- 2,826 individuals trained in TIP prevention
Active program areas
Goals
Strengthen community-based prevention of and response to GBV in eastern Congo
Intermediate result 1
Target communities demonstrate greater acceptance of positive gender roles.
Intermediate result 2
Availability of community-level GBV-related services improved.
Intermediate result 3
Perceptions of stigma surrounding reintegrated survivors reduced.